UC:IS:MaintenancePlanning
| Maintenance Planning (MAPL) Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: RS | |||
| |||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
Maintenance Planning; Wartungsplanung
Description / Beschreibung
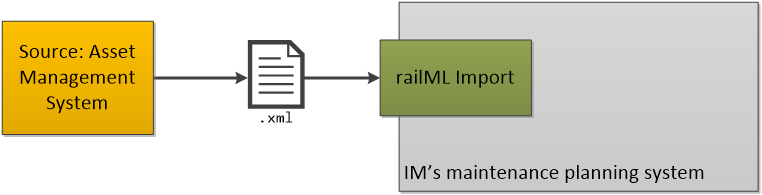
The application focuses the transfer of infrastructure data from an asset management source system (e.g. DfA in Switzerland) to the maintenance planning system of the infrastructure manager.
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
The data flow is one-directional: It goes from the (central) asset management source data base to the maintenance planning system of the infrastructure manager. There are two types of data flows:
- Initial full transfer (realized outside the defined interface, done only once)
- Delta transfer of updated elements
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemen
- rolling stock
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
This section serves to specify the required data regarding certain aspects.
How often do the data change (update)?
- monthly
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- tiny
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- Signaling
- Construction
- Geodasy (coordinates)
Which specific IS data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
- Topology:
- Lines
- Operational points
- tracks
- Asset types:
- Trackbed (“Fahrbahn”)
- Railway electrification system (“Bahnstrom”)
- Signaling (interlockings, signals, signalling components)
- Bridges, tunnels
- Walls, sewing systems
- Station building infrastructure
- Platforms
- Telecommunication infrastructure
- Special railway vehicles:
- Maintenance railway vehicles