Introduction
Documentation
Syntax
Autoexport from the XML-Schema for element IS:loadingGauge of railML ® version 3.2 |
| Documentation
|
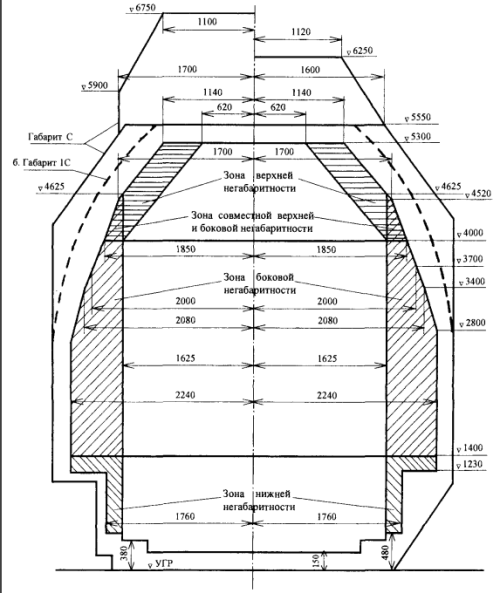
The loading gauge describes the maximum height and width for railway vehicles and their loads to ensure safe passage through bridges, tunnels and other structures.
|
| Subschema
|
|
| Parents*
|
|
| Children
|
areaLocation (0..*), designator (0..*), external (0..*), gmlLocations (0..*), isValid (0..*), kinematicProfile (0..1), linearLocation (0..*), name (0..*), networkLocation (0..*), spotLocation (0..*), staticProfile (0..1), typeDesignator (0..*)
|
Attributes:
- code: code name of the train loading gauge;
use value from the separate codelist file 'TrainClearanceGauges.xml'/trainClearanceGauge (optional; xs:string),
- id: the identifier of the object; this can be either of type xs:ID or UUID (obligatory;
xs:string; patterns: (urn:uuid:)?[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}|{[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}}); compare: Dev:Identities
|
*Notice:
Elements may have different parent elements. As a consequence they may be used in different contexts.
Please, consider this as well as a user of this wiki as when developing this documentation further.
Aspects that are only relevant with respect to one of several parents should be explained exclusively in the documentation of the respective parent element.
|
Autoexport from the XML-Schema for element IS:loadingGauge of railML ® version 3.1 |
| Documentation
|
The loading gauge describes the maximum height and width for railway vehicles and their loads to ensure safe passage through bridges, tunnels and other structures.
|
| Subschema
|
|
| Parents*
|
|
| Children
|
|
Attributes:
- code: code name of the train loading gauge;
use value from the separate codelist file 'TrainClearanceGauges.xml'/trainClearanceGauge (optional; xs:string),
- id: the identifier of the object; this can be either of type xs:ID or UUID (obligatory;
xs:ID; patterns: (urn:uuid:)?[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}|{[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}}); compare: Dev:Identities
|
*Notice:
Elements may have different parent elements. As a consequence they may be used in different contexts.
Please, consider this as well as a user of this wiki as when developing this documentation further.
Aspects that are only relevant with respect to one of several parents should be explained exclusively in the documentation of the respective parent element.
|
Changes 3.1→3.2
The children have changed.
The attributes have been changed.
Semantics
Best Practice / Examples
Additional Information
Notes
Open Issues