UC:IS:Schematic Track Plan
| Schematic Track Plan (SCTP) Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: IL Reported by: JBD | ||||
| ||||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
Schematic Track Plan
Description / Beschreibung
Infrastructure managers use maps for the visualization of their railway infrastructure. These maps comprise:
- Geographic maps
- Geoschematic maps / drawings
- Operational points have geodetic coordinates
- In between, the line layout is schematically interpolated
- Schematic drawings
- All elements have screen coordinates resulting from their complete schematic layout.
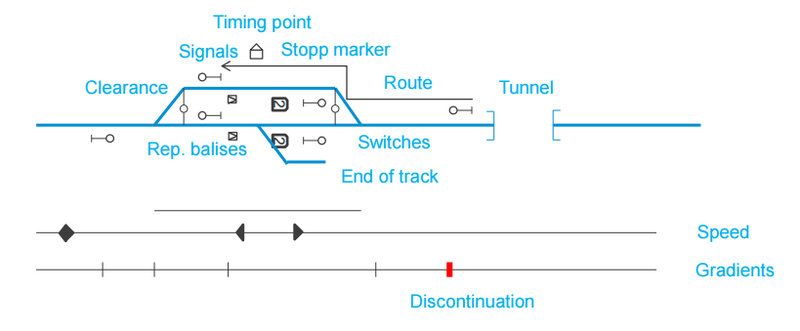
The following figure depicts an example for a schematic drawing:
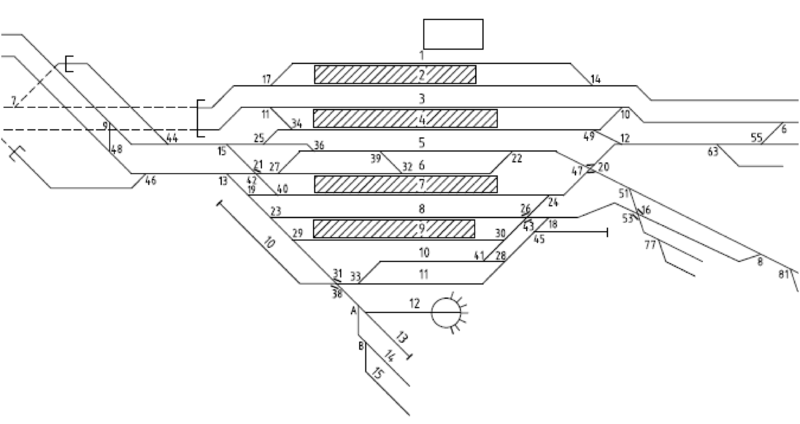
A more complex real world example of a schematic track plan is depicted in the following figure:
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
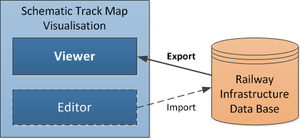
The infrastructure manager uses data from their own data bases to visualize them in the mentioned different types of maps. If the visualizing system comprises also editor functionality, there will be also a feedback channel to import the modified data into the infrastructure manager data bases.
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemen
- IL
This interference to interlocking relates to the visualization of routes and their attributes (ATP device type, CTC handling, overlap/safety zone/slip, timers, speeds), which is demanded by JBV.
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
How often do the data change (update)?
- static (not changing)
- yearly
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- big (station / yard)
- huge (region)
- whole data set (network)
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- topology: track network, line network
- construction: assets along the track / line
- railway operation: designators of tracks and operational points
Which specific data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
The first table lists the elements and attributes required for the pure Schematic Track Plan:
| Element | Attribute | Typical value | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line | Name, code/abbreviation | Bergensbanen, BB | Text |
| Tracks (only main track for macroscopic view) | Number/name, type (main/left main/right main/route track, other station track, siding, buffer/dead end track), track owner | 1,2A,3P | 1-99; +letters A-Z |
| Speed (for multiple speed profiles) | Profile1 (normal), profile2 (plus) profile3 (tilt) | 40,50,70 | 0-300 (in 5 km/h steps, 300 km/h can be extended in future) |
| Gradients | Gradient | 2 ‰ | 0-55‰ today, 0-35‰ for new lines, operational only integers, line planning usually only one decimal |
| Millage change (Discontinuations) | Milage change, direction change | +300 meters, -20 meters | |
| OCP, Timing point of Operational Control Point (OCP) (aka. Station vertex, station cross section) | CrossSection, Ocp name, OCP type, border to uncontrolled area, local areas, work areas | 45,153 Kilometration, Oslo S | Kilometration to the meter |
| Signals | Name,Aspects,Type, | ||
| Clearances (ClearanceGaugeChange) | 35,123 Km | Kilometration to the meter | |
| Switches | Name (number+letter), Km, main track: left/right/(straight), deflecting track: left/right, normal position: left/right, gradient | 1,201a, 35,123 , 1:12 | |
| Tunnels | Name, cross section, contour (rock (rough)/concrete (smooth)), Km from , Km to | Trollunga, 45m², rock | |
| Level crossings | Name, km | Jeløygate, 34,123 Km | |
| Train detection element (Track circuit border / train detector (axle counter)) | Name, km | 301, 34,123 Km | |
| Stop markers | Valid for train length, Km | 220m, 34,123 Km | |
| Platforms | Name/Number, km from, km to, effective km from , effective km to | ||
| Bridges | Name, Km from, Km to | ||
| Derailers | Name, derailing side, Km | ||
| Underpasses | Name, used for track numbers, Km | ||
| Signal locks(separate or under signal type?) | Name/Number, lock type, Km | S1, C, 34,123 | Lock type: A-E |