UC:IS:ExchangeOfPlanningParametersForInterlockingWithSuppliers
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Exchange of planning parameters for interlocking with suppliers Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: IL Reported by: IS | ||
| ||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
Exchange of planning parameters for interlocking with suppliers; Austausch von Planungsparametern für Stellwerke mit Anbietern
Description / Beschreibung
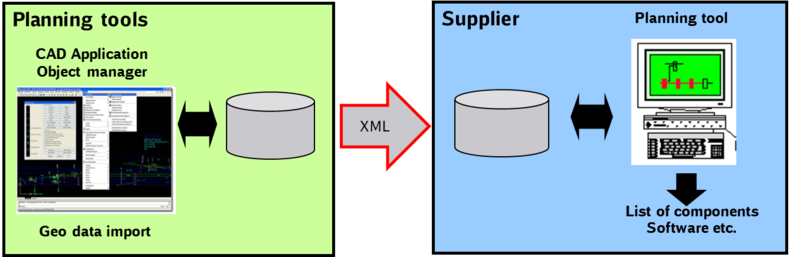
All the planning parameters, which are necessary to build an interlocking (hard- and software), have to be given to the supplier. The content of the data exchange is the result of the planning process, so the data are provided by a specialized planning tool (e.g. ProSig). Further usages for inventory queries are possible.
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
Import into planning tool: geo data, existing planning data, inventory data Export of planning tool: planning data, handing-over to the supplier (by using a database).
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemen
- interlocking (see also: Interlocking Engineering)
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
This section serves to specify the required data regarding certain aspects.
Complete content of a planning for an interlocking:
- Topology and geometry of the track network (2-dimensional) with punctual information about height and superelevation
- Parameters and position of hardware elements (signals, switches etc.)
- Positioning for track-related elements based on topology
- Positioning for other elements based on coordinates
- Parameters of software elements (routes, flank protection for switches etc.)
How often do the data change (update)?
- yearly
- monthly
- weekly
- daily
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- very small (element)
- small (operational point)
- big (station/yard)
- huge (region)
- whole data set (network)
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- Signaling
- Geometry
- Construction
- Statistics
- Energy
- Topology
Which specific IS data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
- Topology of the track network
- Nodes, edges
- Inner topology: connections between edges or marker at edges for correct routing at switches
- Geometry of the track network and lines
- Nodes, edges
- For edges: length, radius/curvature
- Additional: punctual information about height and superelevation
- Infrastructure elements, e. g.
- Platforms and platform edges: position, height, length, identifier for user (e.g. “Bahnsteig A”)
- Signals: name, position, effective direction, type, operational function, signaling system, construction details (e. g. height, fundament type, height of light point, diffusion disc), functional details (e g. passing non-stop allowed, clearance of overlap), energy and information supply
- Switches: e. g. name, type, basic form, isolation, kind of switch signal, operation mode, priority position, radius and possible speed per leg, kind of point machine(s), energy and information supply
- Level crossings: name, position, construction details, functional details, energy and information supply
- Elements of automatic train control: position, construction details, functional details, energy and information supply
- Key locks or lock combination: name, position, energy and information supply
- Bridges, tunnels: position, length along the topology