UC:IS:ETCS track net
| ETCS Track Net (ETCS) Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: IL Reported by: Thales | ||
| ||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
ETCS track net
- ETCS-a: Input for Detailed Design of ETCS Trackside
- ETCS-b: Output of Detailed Design of ETCS Trackside
- ETCS-c: Alignment on Topology and Properties of Trackside Equipment Before ETCS Balise Placement
ETCS track net covers the requirements for access and use of the rail network of the infrastructure manager in microscopic way. It provides all the technical and operational information that is necessary for entities entitled to access the network, determine train positions and generate a movement authority for the train.
On an ETCS equipped railway line, the onboard ATPs are controlled by Movement Authority (MA) messages from a wayside RBC or LEU. These messages contain detailed information about certain aspects of the infrastructure, e.g. balises, speed restrictions, gradients and track conditions. This use case aims at modelling all infrastructure data necessary for generating MAs, as defined by SUBSET-026, version 3.x.
ETCS-a
Data transfer from Infrastructure Manager to Signalling Supplier (input for the start of an ETCS Level 2 trackside project based on a centralized technical solution; Details for ETCS Level 1 to follow with railML V3.3)
ETCS-b
Data transfer from Signalling Supplier to Infrastructure Manager (output as delivery data of an ETCS Level 2 trackside project based on a centralized technical solution; Details for ETCS Level 1 to follow with railML V3.3)
ETCS-c
Data transfer of topology data between Infrastructure Manager and Signalling Supplier(s) (input or control data set as basis for all project members, independent of ETCS Level)
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
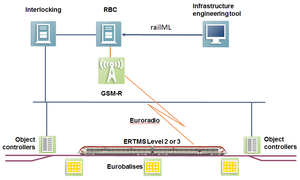
|
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemen
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
How often do the data change (update)?
- Regular changes
ETCS-a
The frequency for updates should be low.
The updates depends on reconstructions of the ETCS area.
ETCS-b
The frequency of updates is high.
The signalling supplier will add application data like balises.
ETCS-c
The frequency for updates should be low.
The updates depends on reconstructions of the ETCS area.
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- Big station (yard)
- Huge (region)
- Whole date set (network)
ETCS-a
The amount of the data to be exchanged match the length of the ETCS area, that means the size and the complexity of the stations.
The element count ranges from the low hundreds up to several thousand data elements per occurrence.
ETCS-b
The amount of the data to be exchanged is bigger than in use case ETCS-a because data such as balises or routes will be added.
ETCS-c
The amount of the data to be exchanged is the same as in use case ETCS-a.
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- Topology: track network, line network
- Construction: assets along the track / line
ETCS-a
- Track layout description
- ETCS level transition locations
- Points
- Signals
- BaliseGroups (if available in this project status)
- Workíng Areas
- Local operation Areas
- Shunting Areas
- Interlockings (if available in this project status)
ETCS-b
- Balise groups
- Routes
- Interlockings
- RBCs
ETCS-c
- Track layout description
- Points
- Signals
Which specific data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
| Element | Attribute | Typical value | Range | ETCS-a | ETCS-b | ETCS-c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common | ||||||
| electrificationSystems | ||||||
| speedProfiles | ||||||
| Topology | ||||||
| netElements | ||||||
| netRelations | ||||||
| networks | ||||||
| Geometry | ||||||
| gradientCurve (slope) | ||||||
| FunctionalInfrastructue | ||||||
| balises | ||||||
| borders | ||||||
| bufferStops | ||||||
| electrifications | ||||||
| levelCrossings | ||||||
| lines | ||||||
| platforms | ||||||
| restrictionAreas | ||||||
| signals | ||||||
| speeds | ||||||
| switches | ||||||
| tracks | ||||||
| trainDetectionElements | ||||||
| Signalling (train radio; communication system) | ||||||
