Introduction
Documentation
Syntax
Autoexport from the XML-Schema for element IL:interlocking of railML ® version 3.3 |
| Documentation
|
root element for railML3 interlocking model
|
| Subschema
|
interlocking
|
| Parents*
|
railML
|
| Children
|
assetsForInterlockings (0..1), controllers (0..1), objectControllers (0..1), radioBlockCentres (0..1), signalBoxes (0..1), specificInfrastructureManagers (0..1)
|
| Attributes:None
|
*Notice:
Elements may have different parent elements. As a consequence they may be used in different contexts.
Please, consider this as well as a user of this wiki as when developing this documentation further.
Aspects that are only relevant with respect to one of several parents should be explained exclusively in the documentation of the respective parent element.
|
Autoexport from the XML-Schema for element IL:interlocking of railML ® version 3.2 |
| Documentation
|
root element for railML3 interlocking model
|
| Subschema
|
interlocking
|
| Parents*
|
railML
|
| Children
|
assetsForInterlockings (0..1), controllers (0..1), radioBlockCentres (0..1), signalBoxes (0..1), specificInfrastructureManagers (0..1)
|
| Attributes:None
|
*Notice:
Elements may have different parent elements. As a consequence they may be used in different contexts.
Please, consider this as well as a user of this wiki as when developing this documentation further.
Aspects that are only relevant with respect to one of several parents should be explained exclusively in the documentation of the respective parent element.
|
Autoexport from the XML-Schema for element IL:interlocking of railML ® version 3.1 |
| Documentation
|
root element for railML3 interlocking model
|
| Subschema
|
interlocking
|
| Parents*
|
railML
|
| Children
|
assetsForIL (0..1), controllers (0..1), signalBoxes (0..1), specificIMs (0..1)
|
| Attributes:None
|
*Notice:
Elements may have different parent elements. As a consequence they may be used in different contexts.
Please, consider this as well as a user of this wiki as when developing this documentation further.
Aspects that are only relevant with respect to one of several parents should be explained exclusively in the documentation of the respective parent element.
|
Changes 3.1→3.2
There exists an overview of all changes between railML® 3.1 and railML® 3.2 on page Dev:Changes/3.2.
The children have been changed.
Changes 3.2→3.3
There exists an overview of all changes between railML® 3.2 and railML® 3.3 on page Dev:Changes/3.3.
The children have been changed.
Semantics
Best Practice / Examples
Additional Information
Notes
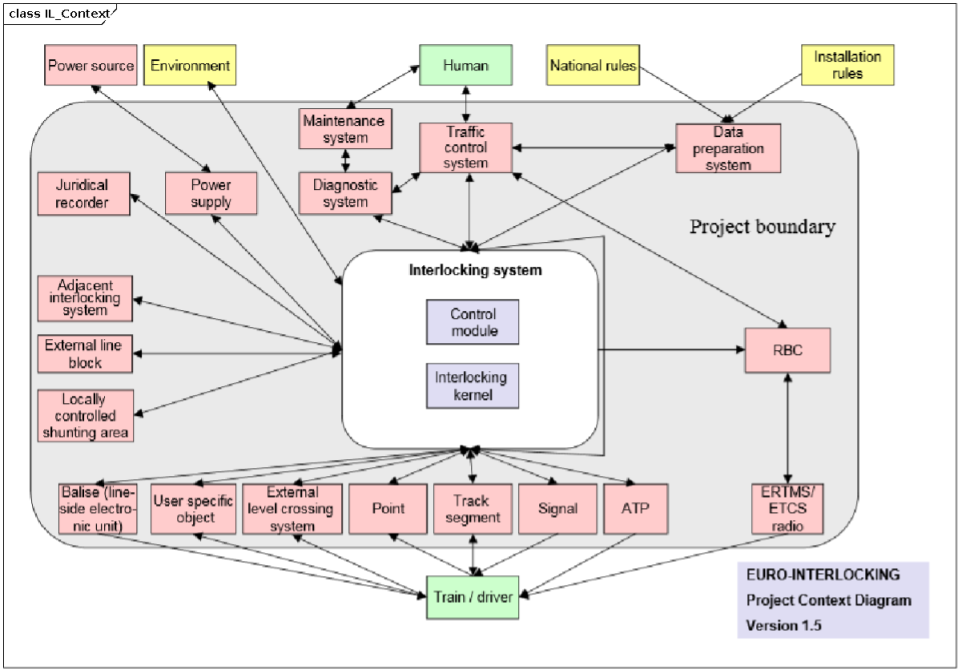
The railML interlocking subschema contains definitions of data describing railway signalling and the use of interlocking systems. There are lot of different objects which will appear in infrastructure and interlocking. As a rule all physical characteristics, which can be "touched" are in infrastructure. All things about function and usage from train control point of view are in interlocking. Interlockings in strict sense are control systems using movable elements, signals, detectors, and other components in combinations and sequences that hinder collision and derailment of trains. Although the entire subschema is called “interlocking” the term “interlocking” is mainly used in this document for the equipment of the interlocking logic.
An interlocking description consists mainly of:
- Track and trackside signalling components,
- Route control logic,
- Interfaces,
- Control system, and
- Controllers.
Each of these categories are described in more detail in sections below.
The base type for interlocking entities in railML® includes the id attribute (see Dev:identities about its use) and the <designator> element, as well as the the possibility to add custom attributes through the xs:anyAttribute mechanism.
Open Issues
