UC:IS:ETCS track net: Difference between revisions
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(Vorbereitung Trennung) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ===ETCS-c=== | ||
{{UC data}} | {{UC data}} | ||
===ETCS-a=== | ====ETCS-a==== | ||
===ETCS-b=== | ====ETCS-b==== | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ====ETCS-c==== | ||
{{UC update}} | {{UC update}} | ||
*Regular changes | *Regular changes | ||
===ETCS-a=== | ====ETCS-a==== | ||
===ETCS-b=== | ====ETCS-b==== | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ====ETCS-c==== | ||
{{UC complexity}} | {{UC complexity}} | ||
*Big station (yard) | *Big station (yard) | ||
*Huge (region) | *Huge (region) | ||
*Whole date set (network) | *Whole date set (network) | ||
===ETCS-a=== | ====ETCS-a==== | ||
===ETCS-b=== | ====ETCS-b==== | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ====ETCS-c==== | ||
{{UC focus}} | {{UC focus}} | ||
*Topology: track network, line network | *Topology: track network, line network | ||
*Construction: assets along the track / line | *Construction: assets along the track / line | ||
===ETCS-a=== | ====ETCS-a==== | ||
===ETCS-b=== | ====ETCS-b==== | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ====ETCS-c==== | ||
{{UC elements}} | {{UC elements}} | ||
;Common | ;Common | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
*trainDetectionElements | *trainDetectionElements | ||
*Signalling (train radio; communication system) | *Signalling (train radio; communication system) | ||
===ETCS-a=== | ====ETCS-a==== | ||
===ETCS-b=== | ====ETCS-b==== | ||
===ETCS-c=== | ====ETCS-c==== | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 16 January 2023
| ETCS Track Net (ETCS) Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: IL Reported by: Thales | |||
| |||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
ETCS track net
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Description / Beschreibung
ETCS track net covers the requirements for access and use of the rail network of the infrastructure manager in microscopic way. It provides all the technical and operational information that is necessary for entities entitled to access the network, determine train positions and generate a movement authority for the train.
On an ETCS equipped railway line, the onboard ATPs are controlled by Movement Authority (MA) messages from a wayside RBC or LEU. These messages contain detailed information about certain aspects of the infrastructure, e.g. balises, speed restrictions, gradients and track conditions. This use case aims at modelling all infrastructure data necessary for generating MAs, as defined by SUBSET-026, version 3.x.
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
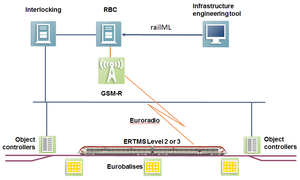
|
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemas
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
How often do the data change (update)?
- Regular changes
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- Big station (yard)
- Huge (region)
- Whole date set (network)
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- Topology: track network, line network
- Construction: assets along the track / line
ETCS-a
ETCS-b
ETCS-c
Which specific data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
- Common
- electrificationSystems
- speedProfiles
- Topology
- netElements
- netRelations
- networks
- Geometry
- gradientCurve (slope)
- FunctionalInfrastructue
- balises
- borders
- bufferStops
- electrifications
- levelCrossings
- lines
- platforms
- restrictionAreas
- signals
- speeds
- switches
- tracks
- trainDetectionElements
- Signalling (train radio; communication system)
