UC:IS:TrafficManagementPlan: Difference between revisions
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{UC elements}} | {{UC elements}} | ||
tbd | tbd | ||
{{interwiki}} | |||
Latest revision as of 11:07, 23 September 2024
| Traffic Management Plan (IMPL) Subschema: Infrastructure Related subschemas: IL TT Reported by: Bombardier | |||
| |||
| For general information on use cases see UC:Use cases |
Use case / Anwendungsfall
Traffic Management Plan
Description / Beschreibung
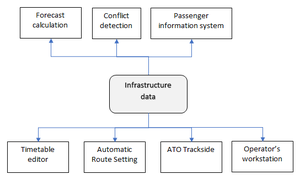
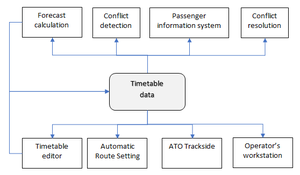
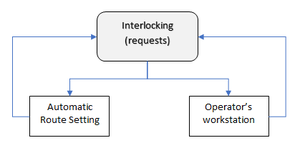
The purpose of a TMS is to optimize rail traffic flow by providing decision support to dispatchers as well as automated functions. Typical tasks of TMS are automatic route setting, real time train graph display, conflict detection, conflict resolution and traffic regulation. For the completeness of the use case, traditional CTC functions are here also considered as part of TMS, i.e. real time track layout display, train describer tracking and command interface for route setting and wayside object control.
This use case aims to cover all data exchange necessary for the functions listed above. A major difference to previous railML use cases is that this includes also real time data, such as positions of trains and states of wayside objects. Hence, the target is not only a static railML file, but also on line data exchange, e.g. by messaging or web services.
Data Flows and Interfaces / Datenflüsse und Schnittstellen
Need to make some drawing here. Main interfaces for TMS is CCS (i.e. IL and RBC), timetable planning system and (optionally) fleet management system.
Interference with other railML® schemas / Interferenz mit anderen railML®-Schemen
- IL
- TT
Characterizing Data / Charakterisierung der Daten
How often do the data change (update)?
- tbd
How big are the data fragments to be exchanged (complexity)?
- tbd
Which views are represented by the data (focus)?
- tbd
Which specific data do you expect to receive/send (elements)?
tbd